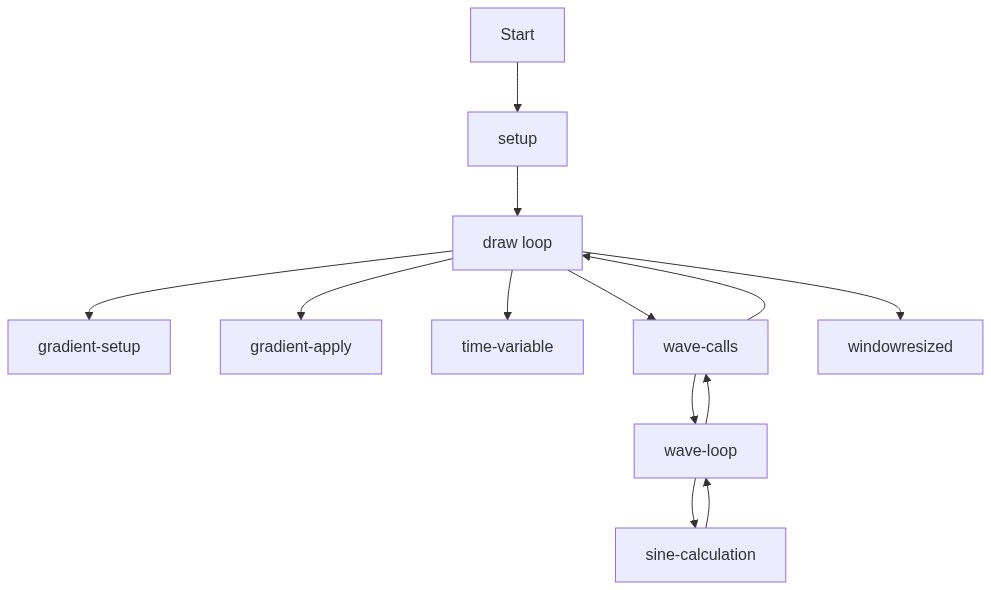
setup()
setup() runs once when the sketch starts. Here we create a full-screen canvas that will display our ocean waves. windowWidth and windowHeight are p5.js variables that automatically contain the browser window's dimensions.
function setup(){createCanvas(windowWidth,windowHeight);}Line by Line:
createCanvas(windowWidth,windowHeight)- Creates a canvas that fills the entire browser window using the current window dimensions