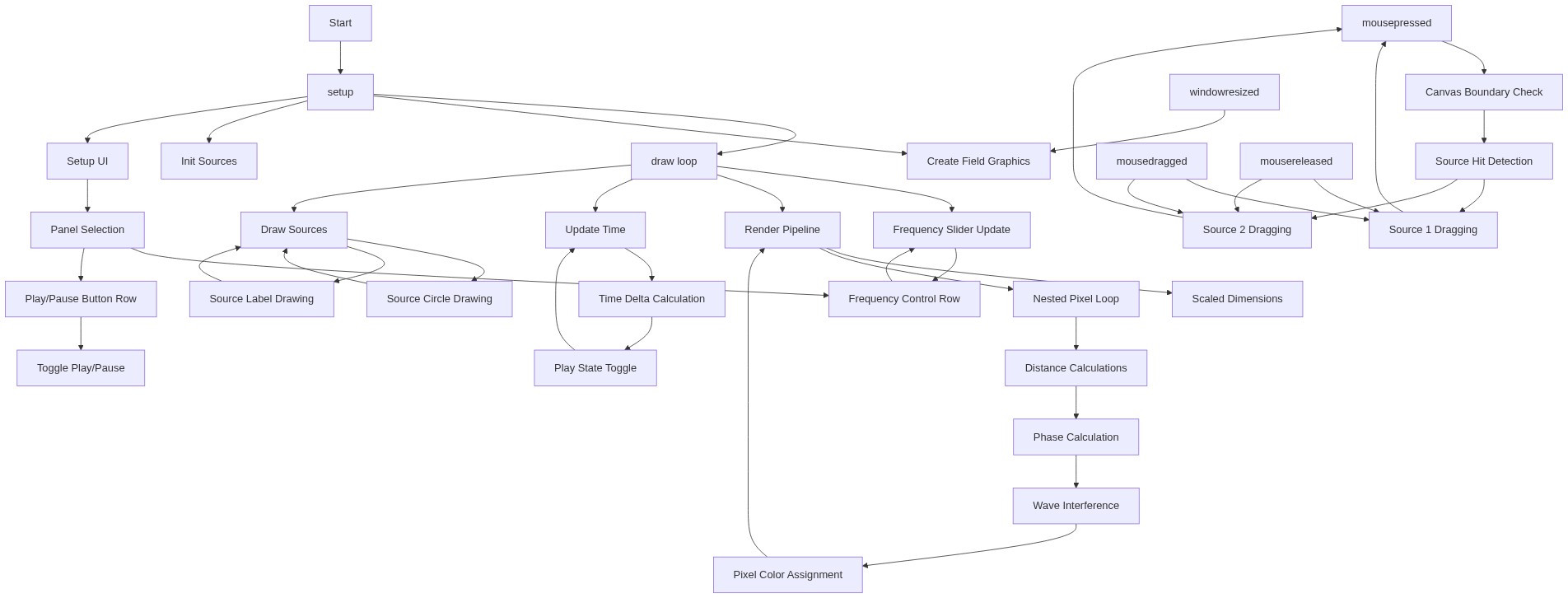
setup()
setup() runs once when the sketch starts. It initializes all the data structures needed for the wave simulation, including the graphics buffer, source positions, and UI controls.
function setup() {
createCanvas(windowWidth, windowHeight);
pixelDensity(1); // make per-pixel math predictable
createFieldGraphics();
initSources();
setupUI();
timeSec = 0;
lastMillis = millis();
}Line by Line:
createCanvas(windowWidth, windowHeight)- Creates a canvas that fills the entire browser window
pixelDensity(1)- Sets pixel density to 1 for predictable pixel-by-pixel calculations (important for interference math)
createFieldGraphics()- Initializes the off-screen graphics buffer where the wave field is computed
initSources()- Sets up the two wave source positions and their properties
setupUI()- Creates the frequency slider and play/pause button in the control panel
timeSec = 0- Initializes the simulation time to zero
lastMillis = millis()- Records the current time in milliseconds to track elapsed time for animation