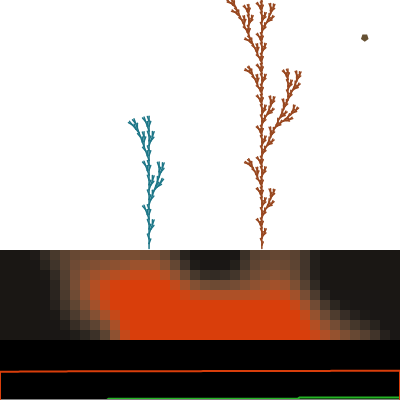
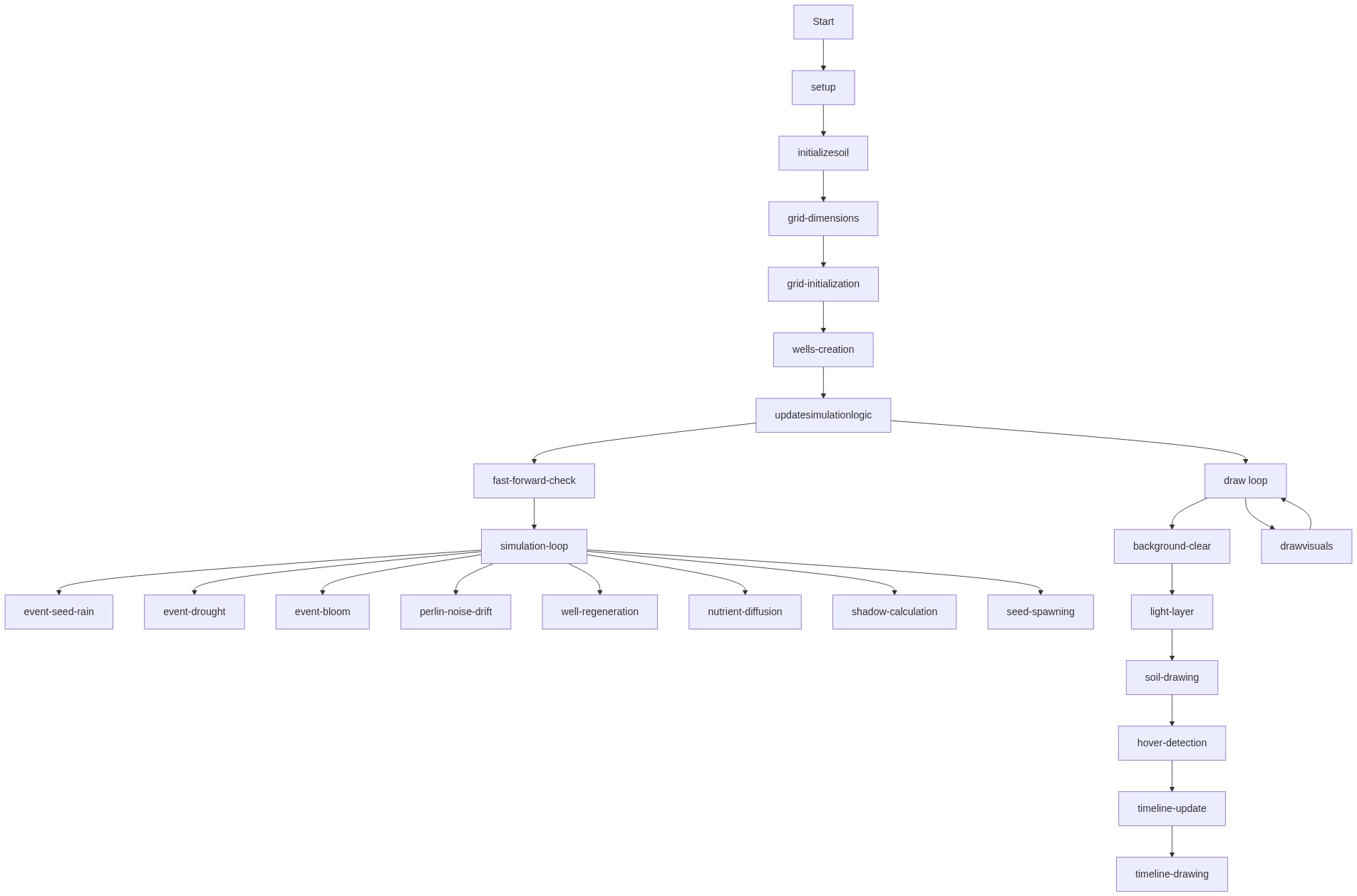
function drawVisuals() {
background(0, 0, 5);
const soilStartY = height - soilHeight;
push();
noStroke();
for (let x = 0; x < width; x += cellSize) {
let brightness = map(noise(x * lightNoiseScale + lightNoiseOffset), 0, 1, lightBrightnessMin, lightBrightnessMax);
fill(0, 0, 100, brightness);
rect(x, 0, cellSize, height);
}
pop();
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
let nutrientValue = soilGrid[i][j];
let currentHue = map(nutrientValue, 0, 100, depletedHue, richHue);
let currentSat = map(nutrientValue, 0, 100, depletedSat, richSat);
let currentBright = map(nutrientValue, 0, 100, depletedBright, richBright);
fill(currentHue, currentSat, currentBright);
rect(j * cellSize, i * cellSize + soilStartY, cellSize, cellSize);
}
}
noStroke();
for (let particle of nutrientParticles) {
particle.draw();
}
if (showGenealogyWeb) {
push();
stroke(0, 0, 50, 15);
strokeWeight(0.5);
for (let plant of plants) {
if (plant.offspringPlantIDs.length > 0) {
for (let offspringID of plant.offspringPlantIDs) {
let offspring = plantIDMap.get(offspringID);
if (offspring) {
line(plant.x, plant.y, offspring.x, offspring.y);
}
}
}
}
pop();
}
for (let plant of plants) {
plant.draw();
}
noStroke();
for (let seed of seeds) {
seed.draw();
}
let hoveredPlant = null;
for (let i = plants.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let plant = plants[i];
if (plant.isAlive || plant.decayTimer > 0) {
if (dist(mouseX, mouseY, plant.x, plant.y) < plantBaseLength * 2) {
hoveredPlant = plant;
break;
}
}
}
if (hoveredPlant) {
push();
translate(mouseX + 10, mouseY + 10);
fill(0, 0, 100, 80);
noStroke();
rect(0, 0, 150, 80);
fill(0);
textSize(10);
textFont('Arial');
text(`Age: ${frameCount - hoveredPlant.birthFrame} frames`, 5, 15);
text(`Seed Type: ${hoveredPlant.seedShape}`, 5, 30);
text(`Light: ${nf(hoveredPlant.lightExposure, 1, 2)}`, 5, 45);
text(`Alive: ${hoveredPlant.isAlive}`, 5, 60);
if (hoveredPlant.offspringPlantIDs.length > 0) {
push();
stroke(0, 0, 50, 50);
strokeWeight(1);
for (let offspringID of hoveredPlant.offspringPlantIDs) {
let offspring = plantIDMap.get(offspringID);
if (offspring) {
line(hoveredPlant.x, hoveredPlant.y, offspring.x, offspring.y);
}
}
pop();
}
pop();
}
push();
translate(0, height - timelineHeight);
fill(0, 0, 0, 50);
noStroke();
rect(0, 0, width, timelineHeight);
const maxAlive = max(aliveHistory);
const maxDead = max(deadHistory);
const maxFertility = max(fertilityHistory);
const maxCombined = max(maxAlive, maxDead, maxFertility);
noFill();
stroke(120, 80, 70);
strokeWeight(2);
beginShape();
vertex(0, timelineHeight);
for (let i = 0; i < aliveHistory.length; i++) {
let x = map(i, 0, historyLength - 1, 0, width);
let y = map(aliveHistory[i], 0, maxCombined, timelineHeight, 0);
vertex(x, y);
}
vertex(width, timelineHeight);
endShape();
stroke(0, 0, 50);
beginShape();
vertex(0, timelineHeight);
for (let i = 0; i < deadHistory.length; i++) {
let x = map(i, 0, historyLength - 1, 0, width);
let y = map(deadHistory[i], 0, maxCombined, timelineHeight, 0);
vertex(x, y);
}
vertex(width, timelineHeight);
endShape();
stroke(richHue, richSat, richBright);
beginShape();
vertex(0, timelineHeight);
for (let i = 0; i < fertilityHistory.length; i++) {
let x = map(i, 0, historyLength - 1, 0, width);
let y = map(fertilityHistory[i], 0, 100, timelineHeight, 0);
vertex(x, y);
}
vertex(width, timelineHeight);
endShape();
pop();
}